Nurturing Roots, Growing Together: Afrocare's Community Wellness Programs & Resources
AfroCare Wise Elderly Wellness and Fitness:
The AfroCare Wise Elderly Wellness and Fitness program includes a variety of social activities designed to keep seniors active, engaged, and connected. These activities cater to the elderly's interests and needs, fostering community and enhancing their quality of life.
The AfroCare Wise Elderly Wellness and Fitness program aims to enhance the life quality of elderly participants.
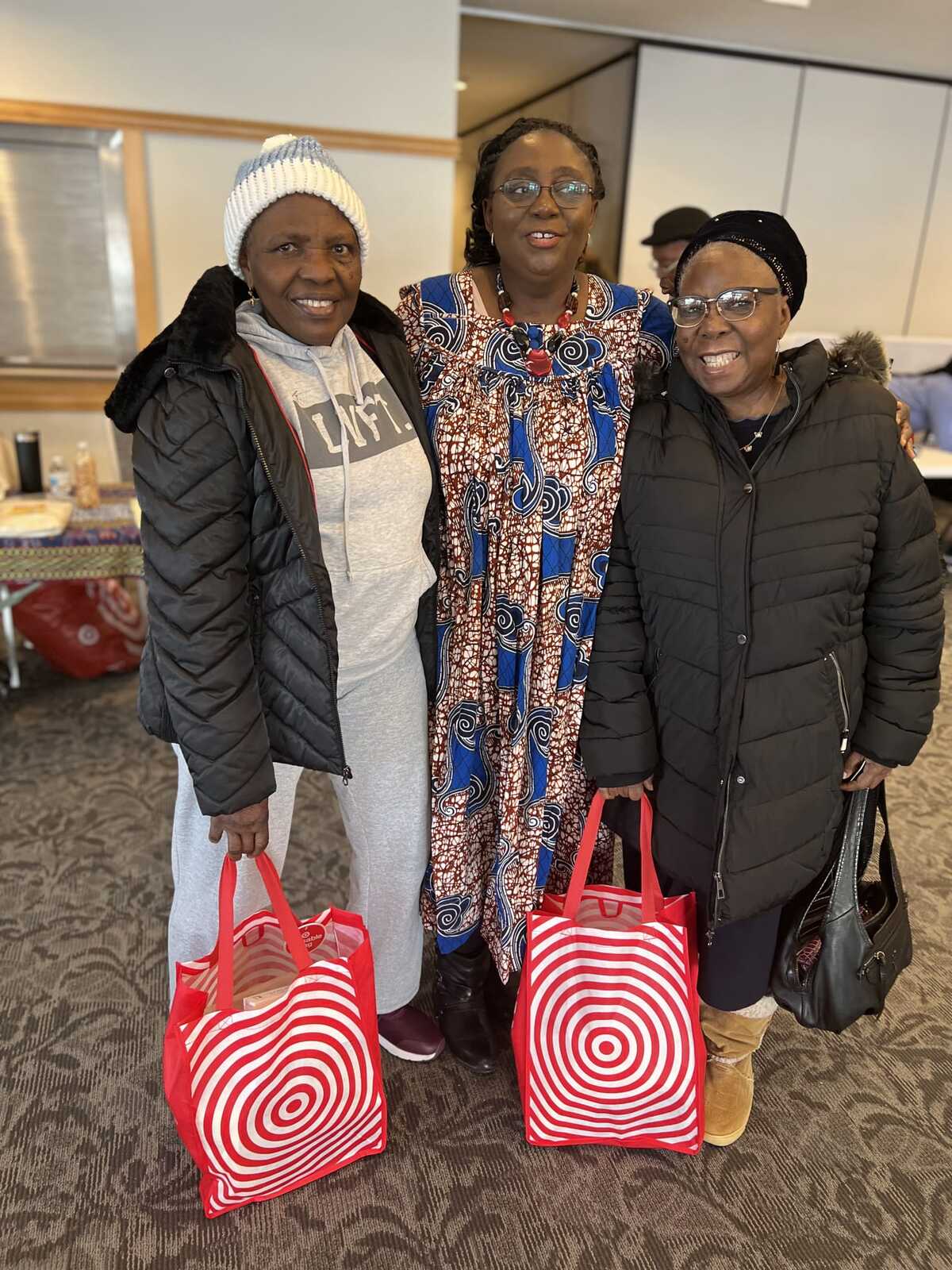

Key Advantages
Reduced Fall Risk: The program has successfully reduced fall risk by 60%, which is a significant achievement in promoting the safety and well-being of seniors. Improved Quality of Life: By keeping seniors active, engaged, and connected through tailored fitness classes and social activities, the program has significantly improved the overall quality of life for elderly participants. Social Engagement: The variety of social activities included in the program helps seniors stay connected and engaged with their peers, fostering a sense of community, and reducing feelings of isolation. Physical Fitness: Fitness classes designed to address the specific needs of elderly participants, assisting them in maintaining and enhancing their physical health. Mental Well-being: The program's focus on social activities and engagement also contributes to the mental well-being of participants, providing them with opportunities for meaningful interactions and support. AfroCare Wise Elderly Wellness and Fitness is a program designed to keep seniors active, engaged, and connected through tailored fitness classes and social activities. The program has successfully reduced fall risk by 60% and significantly improved the quality of life for elderly participants. Chronic disease prevention, management, and education
Extensive Resources

Afrocare provides a suite of resources to help you achieve your goals. Please pick from the menu below to explore.
Anxiety
Symptoms
- Feelings of nervousness, restlessness, or tension
- A sense of impending danger, panic, or doom
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing (hyperventilation)
- Excessive sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Feelings of weakness or fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing on anything other than current worries.
- Sleep disturbances
- Gastrointestinal (GI) issues
- Challenges in managing excessive worry.
- A tendency to avoid situations that trigger anxiety.
- Worries
Psychoeducation
Benefits of Psychoeducation:
Examples of psychoeducation programs:

We are here to help you along the way.
When it comes to managing multiple behavioral health and medical conditions simultaneously, psychoeducation plays a crucial role. Overlapping symptoms can complicate diagnosis, management, and treatment of conditions, often triggering severe mental illness symptoms. Psychoeducation can help individuals with chronic comorbid and co-occurring conditions to adapt to their illnesses, improve self-management, and reduce symptoms.
Family Psychoeducation: This program involves educating family members about mental health conditions, helping them understand the symptoms, treatment options, and ways to support their loved ones. It fosters a supportive environment and encourages open communication.
Individual, Group, Couple and Family Strength-based Support.
Strength-based support is an approach that focuses on the inherent strengths and resources of individuals, groups, couples, and families.
Examples of how AFROCARE would apply this approach in different settings:
- Solution-Focused Therapy (SFT): This approach focuses on finding solutions rather than dwelling on problems. It helps individuals identify their strengths and resources to overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
- Narrative Therapy: This therapy involves helping individuals reframe their personal stories in a more positive light. By focusing on their strengths and achievements, individuals can develop a more empowering narrative about their lives.
- Positive Psychology Interventions: These interventions aim to enhance well-being by focusing on positive aspects of an individual's life, such as gratitude, optimism, and resilience. Techniques may include gratitude journaling, strength identification, and mindfulness practices.
- Strengths-Based Coaching: This type of coaching helps individuals identify and leverage their strengths to achieve personal and professional goals. It involves setting goals, developing action plans, and providing ongoing support and encouragement.
- Motivational Interviewing: This technique helps individuals find motivation for positive life changes. It
- Improved Understanding: Psychoeducation helps individuals understand their mental health conditions, which can reduce anxiety and confusion. It also helps them identify symptoms and understand the nature of their conditions.
- Enhanced Coping Skills: By learning about their conditions, individuals can develop better coping strategies to manage their symptoms. This includes building resilience and developing effective stress management techniques.
- Better Treatment Adherence: When individuals understand their treatment plans, they are more likely to follow through with them. This can lead to improved treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
- Support for Families: Psychoeducation can also be beneficial for family members, helping them understand and support their loved ones more effectively. This fosters a supportive environment and encourages open communication.
- Empowerment and Self-Management: Psychoeducation empowers individuals by increasing their understanding of their own conditions, reducing stigma, and promoting self-management. This can lead to improved self-esteem and a greater sense of control over their lives.
- Strength-Based Approach: Strength-based support focuses on the inherent strengths and resources of individuals, groups, couples, and families. This approach helps build self-esteem, resilience, and coping skills, and encourages individuals to leverage their strengths to overcome challenges.
- Resilience Training: This training focuses on building resilience by helping individuals develop coping strategies and stress management techniques. It emphasizes the importance of self-care, social support, and positive thinking.
Trauma-Informed Care (TIC) and Post-Traumatic Growth (PTG)
PTG can appear in different forms:
- New Opportunities: Survivors of trauma may recognize and embrace new opportunities in their lives.
- Stronger Relationships: They may forge stronger relationships with loved ones and others who have suffered similarly.
- Inner Strength: Individuals often cultivate inner strength through the knowledge that they have overcome tremendous hardship.
- Appreciation for Life: There is often a deeper appreciation for life and its value.
- Spiritual Changes: Their relationship to religion and spirituality may change and evolve.
PTG is different from resilience. While resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity, PTG goes beyond this by representing the capacity to reflect, grow, and truly shift one's perspective. Not everyone who suffers trauma experiences PTG, but for those who do, the changes can be lifelong.Post-Traumatic Growth (PTG) and resilience are related concepts, but they differ in significant ways. PTG is the positive psychological change following a life crisis or trauma. It involves a transformation in understanding oneself, others, and the world, leading to new opportunities, stronger relationships, inner strength, a deeper appreciation for life, and spiritual changes.On the other hand, resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity. It is the process of adapting well in the face of adversity, trauma, tragedy, threats, or significant sources of stress. While resilience involves recovering and returning to a baseline state of functioning, PTG goes beyond this by representing the capacity to reflect, grow, and truly shift one's perspective.
- Cognitive Processing: Encouraging individuals to reframe their traumatic experiences and find meaning in them. This can involve challenging negative beliefs and developing a more positive outlook on life.
- Narrative Development: Helping individuals create a coherent narrative of their trauma. This can involve writing or talking about their experiences, which can aid in processing and integrating the trauma into their life story.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help individuals stay present and reduce anxiety. These practices can also promote self-awareness and emotional regulation.
- Social Support: Building and maintaining strong social connections can provide emotional support and a sense of belonging. Sharing experiences with others who have gone through similar trauma can be particularly beneficial.
- Goal Setting: Encouraging individuals to set and pursue meaningful goals can provide a sense of purpose and direction. Achieving these goals can boost self-esteem and foster a sense of accomplishment.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Engaging in therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Solution-Focused Therapy (SFT), and trauma-focused therapies can provide structured support and guidance in fostering PTG.
- Spiritual and Existential Exploration: Exploring spiritual or existential beliefs can help individuals find deeper meaning and purpose in life. This can involve engaging in religious practices, meditation, or philosophical reflection.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can improve mental health and well-being. Exercise can reduce stress, improve mood, and promote overall physical health.
Chronic Disease Prevention, Management, and Education
Chronic Disease Prevention, Management, and Education is a crucial aspect of the AfroCare Wise Elderly Wellness and Fitness program. This component focuses on providing seniors with the knowledge and tools they need to prevent, manage, and understand chronic diseases. The program includes educational sessions on various chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis, and offers strategies for managing these conditions effectively. By empowering seniors with this information, the program aims to improve their overall health and quality of life.

Managing chronic diseases involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and educational strategies. AFROCARE promotes the following strategies:
- Ethnic Pantry for Healthy food: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products can help manage and prevent chronic diseases. Limiting added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium is also important.
- The use of Pedometer to encourage Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or gardening, for at least 150 minutes a week can help prevent, delay, or manage chronic diseases. Muscle-strengthening activities are also beneficial.
- Quit Smoking: Stopping smoking or never starting can significantly lower the risk of serious health problems, such as heart disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes, and lung disease.
- Limit Alcohol: Reducing alcohol consumption can help prevent high blood pressure, various cancers, heart disease, stroke, and liver disease.
- Regular Screenings: Visiting your doctor and dentist regularly for preventive services can help catch chronic diseases early or prevent them altogether.
- Manage Blood Pressure: Understanding and controlling high blood pressure is crucial for preventing heart disease and stroke.
- Control Cholesterol: Managing cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Reduce Blood Glucose: Monitoring and managing blood glucose levels can help prevent complications related to diabetes.
- Get Enough Sleep: Ensuring at least 7 hours of sleep daily can help manage diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and depression.
- Know Your Family History: Sharing your family health history with your doctor can help take steps to prevent or catch chronic diseases early.


Living Well with Chronic Conditions
Living Well with Chronic Conditions refers to a comprehensive approach to managing long-term health conditions in a way that improves overall well-being and quality of life. Living Well with Chronic Conditions aims to enhance the self-management abilities of individuals with long-term health problems. Conditions such as arthritis, mental health issues, chronic pain, cancer, or diabetes can lead to long-term physical decline and health problems. This program teaches new strategies that will give participants the confidence, motivation, and skills needed to manage living with chronic health conditions to develop strategies for feeling your best and connect with others who will support your journey.
This concept emphasizes the importance of self-management, which includes making informed decisions about health, adhering to action plans, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Key components of living well with chronic conditions include:
- Healthy Eating: Following a balanced diet that meets nutritional needs and supports overall health.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise to improve physical fitness and manage symptoms.
- Stress Management: Implementing techniques to reduce stress and improve mental health.
- Adherence to Treatment Plans: Taking medications as prescribed and following medical advice.
- Regular Health Monitoring: Keeping track of health indicators such as blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and other relevant metrics.
- Support Networks: Building and maintaining dedicated support systems, including family, friends, and healthcare providers.
Living Well with Chronic Conditions is a Chronic Disease Self-Management Program, created by Stanford University and overseen by the Self-Management Resource Center.
About the class
This six-week class meets once a week for two and a half hours. Each class includes a new topic designed to help participants deal with chronic conditions. The class is a combination of presentations, discussion, and activities with others who have similar experiences. Participants make weekly action plans, share experiences, and help each other solve problems they encounter in creating and conducting their plan.
You will learn about:
- Dealing with frustration, fatigue, pain, and isolation
- Exercises for improving strength, flexibility, and endurance.
- Use of medications
- Communicating effectively with family, friends, and health professionals
- Nutrition
- How to evaluate new treatments
- A telephone version offered.

Benefits of the class
- Learn how to deal with chronic condition diagnosis.
- Learn strategies for living well even with health difficulties.
- Meeting new friends
- Provide support and encouragement to your peers.
- Become more involved in your community with your neighbors.

Who should take the class?
This class is for anyone who wants to improve their health and quality of life through managing their chronic conditions. It is particularly suited for people who have:
- Pre-diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Depression
- Hypertension
- Cancer
- Arthritis
- Diabetes
- Or another health condition that you would like to better manage.
CDC Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)
The CDC Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) is a comprehensive initiative designed to help individuals at elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The program focuses on making lasting lifestyle changes to improve health and prevent the onset of diabetes. The CDC Diabetes Prevention Program is a valuable resource for anyone looking to take initiative-taking steps to prevent type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health.
Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) group classes, which consist of 12 to 16 participants. Each class led by two qualified instructors, one of whom is typically a peer leader with personal experience in managing diabetes. Participants encouraged to develop weekly action plans, share their experiences, and collaboratively address challenges related to their self-management efforts. Physicians reviewed the course materials, diabetes educators, dietitians, and other healthcare professionals associated with Stanford and the local community.
The PreventT2 curriculum is based on the original 2002 Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) trial and follow-up studies. It promotes modest weight loss (5%–7%) and increased physical activity through a 12-month lifestyle change program.

It is important to note that specific eligibility criteria may vary depending on the program provider. For detailed eligibility requirements for the CDC Diabetes Prevention Program, please check with the program provider.
Who can participate in the DPP program?
- Age: Participants are usually adults aged 18 years or older.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): A BMI of 25 or higher (23 or higher if Asian American).
- Blood Test Results: Participants may need to have blood test results indicating prediabetes, such as:
- Hemoglobin A1C between 5.7% and 6.4%
- Fasting plasma glucose between 100 and 125 mg/dL
- Two-hour plasma glucose between 140 and 199 mg/dL (after a 75-gm glucose load)
- History of Gestational Diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy may also be eligible.
- Risk Test: May use a risk test to determine eligibility based on factors such as age, weight, family history, and physical activity levels.
Find a Program
Locate a CDC-recognized lifestyle change program at https://yourjuniper.org/ and programs on the CDC's National Diabetes Prevention Program website.
Enroll
Participation
Once enrolled, you will join a group of participants and work with an AFROCARE trained lifestyle coach. The program typically lasts one year, with the first six months focusing on intensive lifestyle changes and the following six months on maintaining those changes.
Benefits of the CDC Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP):
- Reduced Risk of Diabetes: Participants who complete the program can significantly reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Research has shown that participants can reduce their risk by 58%, and those over 60 years old can reduce their risk by 71%.
- Improved Health: The program focuses on making lasting lifestyle changes, including healthy eating, physical activity, and stress management. These changes can lead to improved overall health and well-being.
- Support and Motivation: The DPP emphasizes the importance of group support. Participants join a group of people with similar health goals, providing motivation and encouragement to stay on track.
- Long-Term Commitment: The DPP program designed to be a long-term commitment, typically lasting one year. The first six months focus on intensive lifestyle changes, followed by six months of maintaining those changes.
- Accessibility: The program is available in various formats, including in-person, online, and through telehealth, making it accessible to a wide range of individuals.
"Life can be a rollercoaster, full of twists and turns. When the world seems chaotic, it helps to have a guiding light."
Dalai Lama